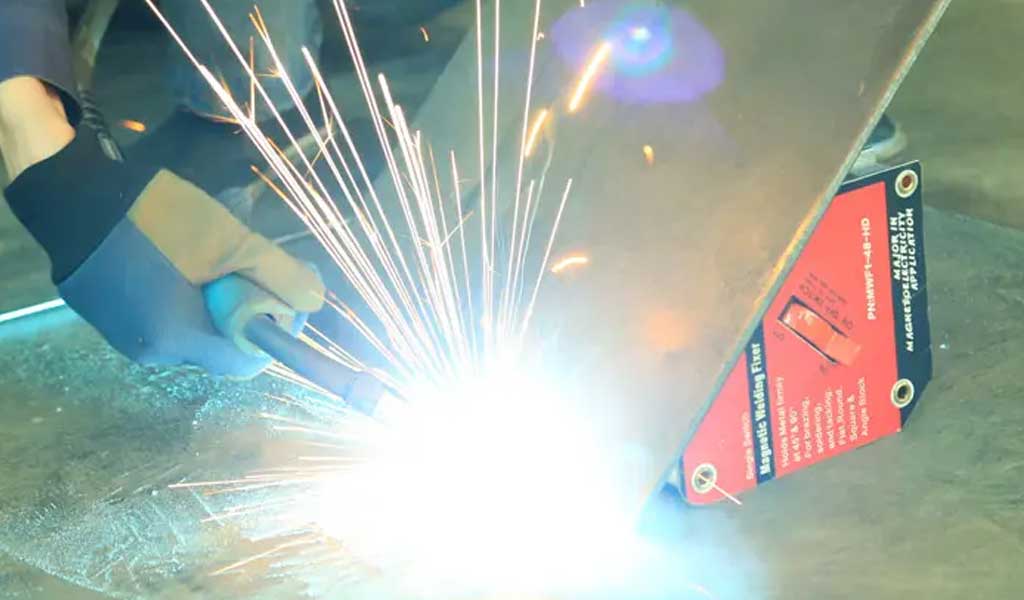
When it comes to laser cutting, what comes to your mind? A laser gun/laser sword that can easily cut through thick walls in sci-fi movies?
Is the laser in reality really so magical, can it achieve “everything” like the laser in the movie? In fact, laser cutting has become a more common application in the real society. Thanks to the versatility of the laser, the laser can quickly and accurately cut through the small non-metallic materials such as paper, wood, glass, etc., as well as thin, thick, soft and hard metal materials.
What Is Laser Cutting?
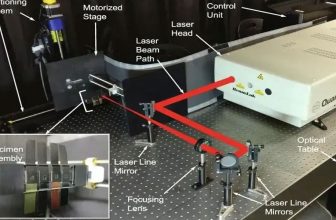
Laser cutting is a non-contact processing method with high energy and density controllability. It uses a focused high power density laser beam to irradiate the workpiece to rapidly melt, vaporize, ablate or reach the ignition point of the irradiated material. The coaxial high-speed airflow of the beam blows away the molten material, thereby cutting the workpiece, which has the advantages of high precision, fast speed, smooth section, high adaptability, and one-time molding.
The development of the laser industry is becoming more and more dynamic, and the changes in laser technology are also changing with each passing day.
After 2011, fiber laser cutting equipment emerged, gradually replacing CO2 laser cutting technology.
After 2015, the 6000W fiber laser cutting machine came out, and basically it can meet the cutting process of most metal materials.
In 2018, Han’s Laser, Xunlei Laser, Pentium Laser, Bystronic Dineng, etc. successively launched 10,000-watt laser cutting machines with larger format and higher power.
After more than 10 years of development, laser cutting is no longer a concept hype that only appears in science fiction films, and is now gradually replacing traditional manual and mechanical knife cutting, and is widely used in sheet metal processing, vehicle manufacturing, construction machinery, kitchenware processing, Advertising customization and many other fields.
What Are The Types Of Laser Cutting?
Generally speaking, laser cutting can be divided into four categories: laser vaporization cutting, laser melting cutting, laser oxygen cutting and laser scribing and controlled fracture.
Laser vaporization cutting is generally suitable for the cutting of extremely thin metal materials and non-metallic materials (such as paper, cloth, wood, etc.). Laser melting cutting is mainly used for the cutting of some easily oxidized materials or active metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum and its alloys. Laser oxygen cutting is mainly used for some difficult-to-cut materials, such as carbon steel, titanium steel and heat-treated steel and other easily oxidized metal materials. Laser scribing and controlled fracture are mainly used in brittle materials that are susceptible to thermal damage.