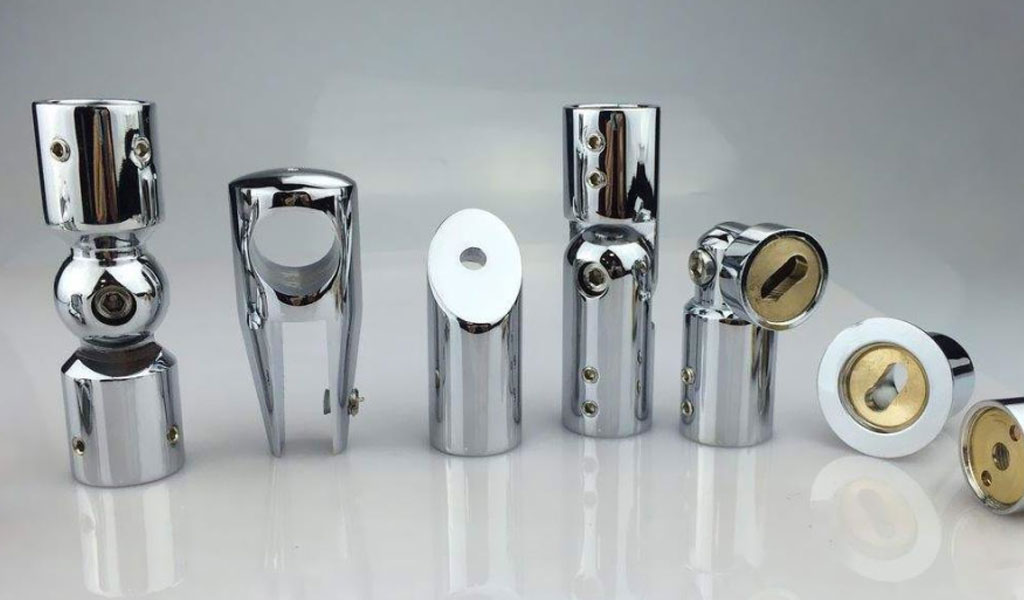
Welding of dissimilar metals refers to the operation of welding two or more different types of metals. Due to the advanced nature of laser welding technology, laser welding of dissimilar metals has become more common in production and life.
Laser welding of dissimilar metals needs to weld two completely different metal materials together, and a transition layer with different properties and structures from the base metal will occur in the middle. Different differences, compared with similar metal welding, the process is very complicated in both welding principle and operation technology.
Main Problems Existing In Dissimilar Metal Laser Welding
1.The greater the difference in the coefficient of linear expansion of dissimilar metal materials, the greater the difficulty of welding
During laser welding of dissimilar metals, the greater the linear expansion coefficient of the material, the greater the thermal expansion rate, and the greater the shrinkage during cooling, which will generate a relatively large welding stress when the molten pool crystallizes. Moreover, this stress is not easy to eliminate, which will cause hidden dangers of welding deformation.
2.The inherent melting point of dissimilar metal materials is positively correlated with the difficulty of welding
In the process of dissimilar metal laser welding, when a metal material with a low melting point reaches the melting point and enters a molten state, the other material with a high melting point remains solid. In this case, the molten material liquid is easy to Penetration into the grain boundaries of the superheated zone can lead to loss of material with a low melting point, burnout or gasification of alloying elements, making welding difficult to complete. For example, the welding of iron material and lead material is very difficult. The two materials are not only insoluble in each other in the solid state, but also insoluble in each other in the liquid state.
3.The greater the difference between the thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity of dissimilar metals, the more difficult it is to weld
The crystallization of the metal is affected by the thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity of the metal material, and also affects the wetting properties of the refractory metal, which in turn affects the quality of the weld. Therefore, when dissimilar metal laser welding, a strong heat source should be used for welding, and the position of the heat source should be biased towards materials with good thermal conductivity during welding.
4.When dissimilar metals are welded, it is difficult to achieve the same strength as the weld and the two base metals.
Metal elements with low melting point are more prone to high temperature and evaporation during laser welding of dissimilar metals, thereby changing the chemical composition of the weld and reducing the mechanical properties, especially when welding different non-ferrous metals.
5.The dissimilar metals with greater electromagnetic difference are more difficult to weld
When dissimilar metals are laser welded, the greater the difference in the electromagnetic properties of the materials, the instability of the welding is likely to occur, which affects the quality of the weld.