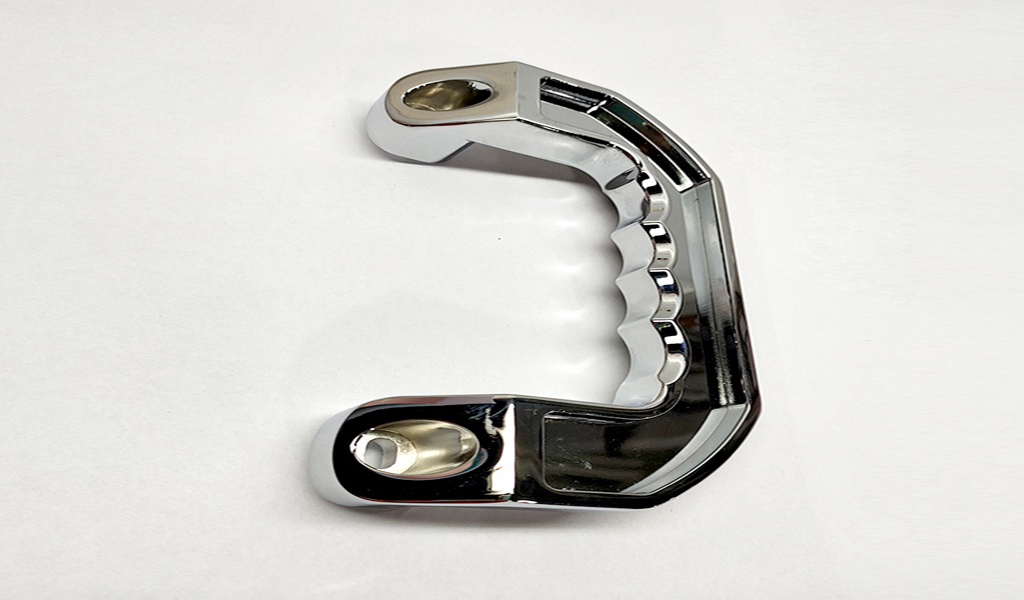
The stamping process can be roughly divided into two categories: separation process and forming process (also divided into bending, deep drawing, and forming). The separation process is to separate the stamping part and the blank from each other along a certain contour line during the stamping process, and the quality of the separated section of the stamping part must also meet certain requirements; the forming process is to make the stamping blank plastic deformation under the condition of no damage, And convert it into the required finished shape, and at the same time, it should also meet the requirements of dimensional tolerance and so on.
According to the temperature during stamping, there are two methods: cold stamping and hot stamping. This depends on the strength, plasticity, thickness, degree of deformation and equipment capacity of the material, etc., and the original heat treatment state and end-use conditions of the material should be considered.
The fabrication of cold stamped metal at room temperature is generally suitable for blanks with a thickness of less than 4mm. The advantages of automobile stamping parts are that there is no need for heating, no oxide scale, good surface quality, convenient operation and low cost. The disadvantage is that there is work hardening, and in severe cases, the metal loses its ability to further deform. Cold stamping requires that the thickness of the blank is uniform, the fluctuation range is small, and the surface is smooth, spotless, and scratch-free.
2. Hot stamping is a stamping method in which the metal is heated to a certain temperature range. The advantages are that it can eliminate internal stress, avoid work hardening, increase the plasticity of the material, reduce the deformation resistance, and reduce the power consumption of the equipment.
Die structure: A die is a tool that separates or deforms the sheet metal. A typical die structure is shown in Figure 3-17, which consists of an upper die and a lower die. The die handle of the upper die is fixed on the slide block of the punch press and moves up and down with the slide block, and the lower die is fixed on the workbench of the punch press.
The punch and the die are the working parts in the die that deform or separate the blank, and are respectively fixed on the upper and lower template by pressing plates. The upper and lower die plates are respectively equipped with guide sleeves and guide posts to guide the alignment of the punch and the die. The guide plate and the positioning pin are used to control the feeding direction and feeding length of the blank, respectively. The function of the stripper is to release the workpiece or blank from the punch after punching.
Die classification
Stamping die is an indispensable die in stamping production. Punching dies can be basically divided into three types: simple dies, continuous dies and composite dies.
- (1) Simple die A simple die is a die that only completes one process in one stroke of the punch. That is, a simple die for blanking or punching. When working, the strip is fed between the two guide plates 9 on the die until it hits the positioning pin 10. When the punch is punched down, the punched parts (or scrap) enter the die hole, while the strip clamps the punch and moves back up with the punch. When the strip hits the stripper plate 8 (fixed on the die), it is pushed down, so that the strip continues to be fed between the guide plates. Repeat the above action to punch down two parts.
- (2) In one stroke of a continuous die punch, a die that simultaneously completes several stamping processes on different parts of the die is called a continuous die. When working, the positioning pin 2 is aligned with the pre-punched positioning hole, the upper die moves downward, the punch 1 is blanked, and the punch 4 is punched. When the upper die returns, the stripper plate 6 pushes the scrap from the punch. At this time, the blank 7 is fed forward again, and the second blanking of the automobile sheet metal part is performed. This cycle is carried out, and each feeding distance is controlled by the stopper pin.
- (3) Composite die In one stroke, a die that simultaneously completes several stamping processes on the same part of the die is called a composite die. The major feature of the composite mold is that there is a convex and concave mold 1 in the mold. The outer circle of the punch and concave die is the cutting edge of the blanking punch die, and the inner hole becomes the deep drawing die. When the slider moves down with the punch and die, the strip is first blanked in the punch and die 1 and the blanking die 4. The blanking part is held up by the deep drawing punch 2 in the lower die, and when the slider continues to move downward, the die moves downward for deep drawing. The ejector 5 and the unloader 3 push the drawn part 9 out of the die during the return stroke of the slide. The compound die is suitable for stamping parts with large output and high precision.
Basic stamping process The main basic processes of stamping are blanking, punching, bending and deep drawing.
- (1) Blanking and punching Blanking and punching are processes for separating blanks.
- The process of blanking and punching is exactly the same, but the purpose is different. When blanking, the separated part is the finished product, and the rest of the periphery is scrap; punching is to obtain holes, the punched sheet is the finished product, and the separated part is scrap. Blanking and punching are collectively referred to as blanking. The punch and the die of the blanking die have sharp edges, and there is a gap of 5%-10% of the thickness of the plate between the punch and the die to ensure neat cuts and less burrs.
- (2) Bending is to make the workpiece obtain various shapes of corners. The working part of the bending die that bends the workpiece should have an appropriate fillet radius r to avoid cracking when the workpiece is bent.
- (3) Deep drawing: Deep drawing is the process of making a flat blank into a cup-shaped or box-shaped part. The punch and die edges of the drawing die should be rounded to prevent the workpiece from being pulled apart. There should be a gap slightly larger than the thickness of the sheet (usually 1.1-1.2 times the thickness of the sheet) between the punch and the die to reduce friction. In order to prevent wrinkling, the edge of the blank needs to be pressed with a pressing plate (crimping ring).
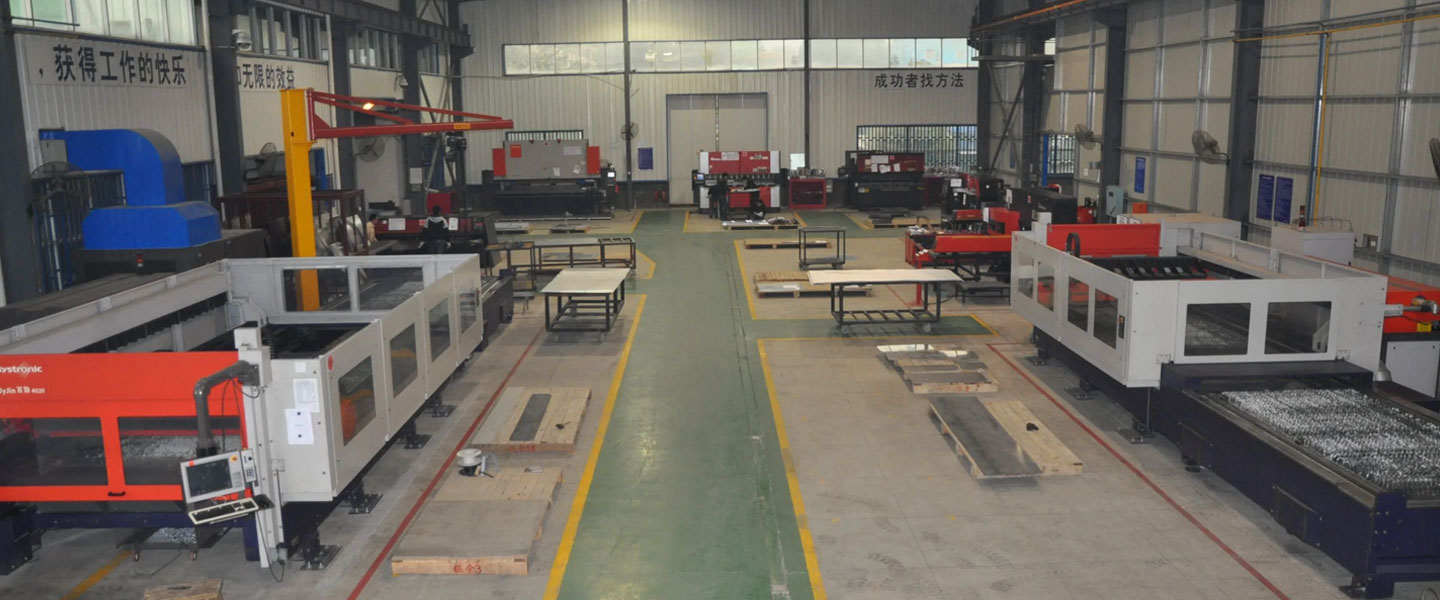

Pintejin Sheet Metal shop offers a cost-effective solution for a wide range of industries with our custom metal stamping and custom sheet metal fabrication capabilities. Our stampnig operations include a variety of sheet-metal forming manufacturing processes, such as punching, blanking, embossing, bending, flanging, and coining. Our professional, experienced and well-trained engineers can execute the complex metal stamping operations with precision and accuracy.
No matter what your metal fabrication needs are, Pintejin can offer the right solution: from single sheet metal part or sub-assembly of stamped metal parts to turnkey solutions for mechanical and electrical assemblies. We have the technology, equipment and the experience to fabricate customised metal products from aluminium sheet metal fabrication, steel, zinc plated steel, stainless steel sheet metal fabrication, brass and copper. Designs that require CNC machining of surfaces or components can be accommodated. We can supply polished, galvanized, zinc coated or powder coated finishes for any sheet metal work or stamped metal components. Coupled with our accurate and reliable metal fabricating equipment, we guarantee precision and repeatability in custom sheet metal work. You’ll be taking advantage of the best sheet metal fabrication china can produce.