In the realm of precision manufacturing, the utilization of advanced technologies has revolutionized the production of intricate and delicate components. Among these cutting-edge methods, Micro Laser Cutting and Micro Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining stand out as highly efficient techniques. Both processes are instrumental in crafting miniature parts with exceptional precision, yet they possess unique characteristics and functionalities that cater to different manufacturing needs. This article aims to delve into an extensive comparison between Micro Laser Cutting and Micro CNC Machining, exploring their principles, applications, advantages, limitations, and the factors influencing their suitability in diverse industrial settings.
Understanding Micro Laser Cutting
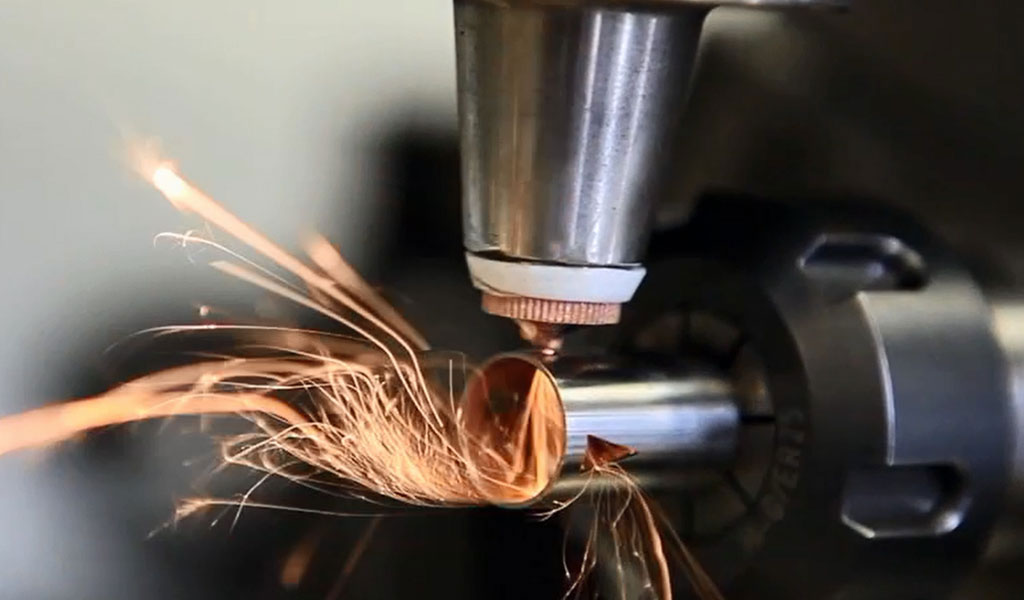
Micro Laser Cutting, an advanced form of laser technology, involves the utilization of a highly focused laser beam to precisely cut through materials with micron-level accuracy. The process typically employs lasers such as CO2, fiber, or ultrashort-pulsed lasers, enabling the creation of intricate designs on various materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and semiconductors.
The mechanism behind Micro Laser Cutting relies on the thermal energy generated by the concentrated laser beam. As the laser interacts with the material’s surface, it melts, vaporizes, or ablates the targeted areas, producing precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. This method proves particularly advantageous when intricate designs or complex geometries are required, owing to its non-contact nature and ability to work with diverse materials.
Applications and Advantages of Micro Laser Cutting
Micro Laser Cutting finds extensive applications across multiple industries, including electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and automotive sectors. Its ability to cut intricate patterns in miniature components, such as microelectronics, microfluidic devices, stents, and sensors, highlights its significance in producing high-precision parts with minimal material waste.
The advantages of Micro Laser Cutting are manifold. Firstly, its non-contact process minimizes mechanical stress on the material, reducing the risk of deformation. Secondly, the precision and accuracy achievable through laser cutting facilitate the production of intricate designs, tiny holes, and fine contours that might be unattainable using conventional methods. Furthermore, the absence of tool wear and the ability to work with a wide range of materials enhance its versatility in various manufacturing applications.
However, Micro Laser Cutting Technology also presents certain limitations. Materials with high reflective properties, such as copper or highly transparent materials like glass, might pose challenges due to the absorption or transmission of the laser beam. Additionally, the initial investment cost for laser equipment and maintenance can be relatively high, potentially impacting the economic feasibility of this method for certain production volumes.
Exploring Micro CNC Machining
On the other hand, Micro CNC Machining involves the utilization of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems to precisely carve and shape materials into intricate designs using rotating cutting tools. This subtractive manufacturing process operates by translating computer-aided designs (CAD) into precise movements of the cutting tools along multiple axes (X, Y, Z) to sculpt the desired component from a solid block or billet.
The heart of Micro CNC Machining lies in its ability to create precise and complex geometries on various materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites. It employs tools such as end mills, drills, and lathes to remove material from the workpiece, allowing for the production of intricate parts with high accuracy.
Applications and Advantages of Micro CNC Machining
Micro CNC Machining serves a broad spectrum of industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, where the demand for high-precision components is paramount. Its applications range from manufacturing micro gears, connectors, implants, to producing molds and prototypes with exceptional accuracy and surface finish.
The advantages of Micro CNC Machining lie in its ability to produce high-precision parts with excellent repeatability. The process offers versatility in material selection, allowing for the machining of various metals, alloys, and engineering plastics. Additionally, CNC machines can execute multiple operations sequentially, reducing the need for manual intervention and ensuring consistency in production.
Nonetheless, Micro CNC Machining also presents certain limitations. The process might encounter challenges in creating highly intricate designs or features with tight tolerances due to limitations in tool size and accessibility. Moreover, the process involves mechanical contact between the cutting tool and the workpiece, which can lead to tool wear over time, necessitating periodic tool changes and affecting dimensional accuracy.
Factors Influencing Choice Between Micro Laser Cutting and Micro CNC Machining
The selection between Micro Laser Cutting and Micro CNC Machining hinges on several crucial factors:
- Material Type and Thickness: Micro Laser Cutting proves advantageous for a wide range of materials, while Micro CNC Machining might be limited by material properties and thickness.
- Design Complexity and Precision: Laser Cutting excels in intricate designs, whereas CNC Machining offers precision but might face limitations in highly complex geometries.
- Cost Considerations: Initial investment, maintenance costs, and production volumes significantly influence the economic feasibility of each method.
- Surface Finish Requirements: CNC Machining may produce better surface finishes, while Laser Cutting can introduce minimal heat-affected zones depending on the material.
- Production Volume and Lead Time: For low to medium volumes and quick prototyping, Micro CNC Machining might be more suitable, while Micro Laser Cutting could be efficient for higher volumes due to its speed and automation capabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Micro Laser Cutting vs Micro CNC Machining stand as pivotal technologies in precision manufacturing, each offering unique advantages and limitations. The selection between these methods depends on specific application requirements, material characteristics, design intricacies, and economic considerations. Industries seeking high-precision components with intricate designs must carefully evaluate the merits of each method to determine the most suitable approach for their production needs. As technology advances, these methods continue to evolve, promising further enhancements in precision, efficiency, and versatility, reshaping the landscape of precision manufacturing.
The synergistic integration of these advanced techniques with ongoing technological innovations is poised to drive forward the frontier of precision manufacturing, enabling the creation of increasingly intricate and precise components that power diverse industries around the globe.